Defend the digital landscape against evolving cyber threats
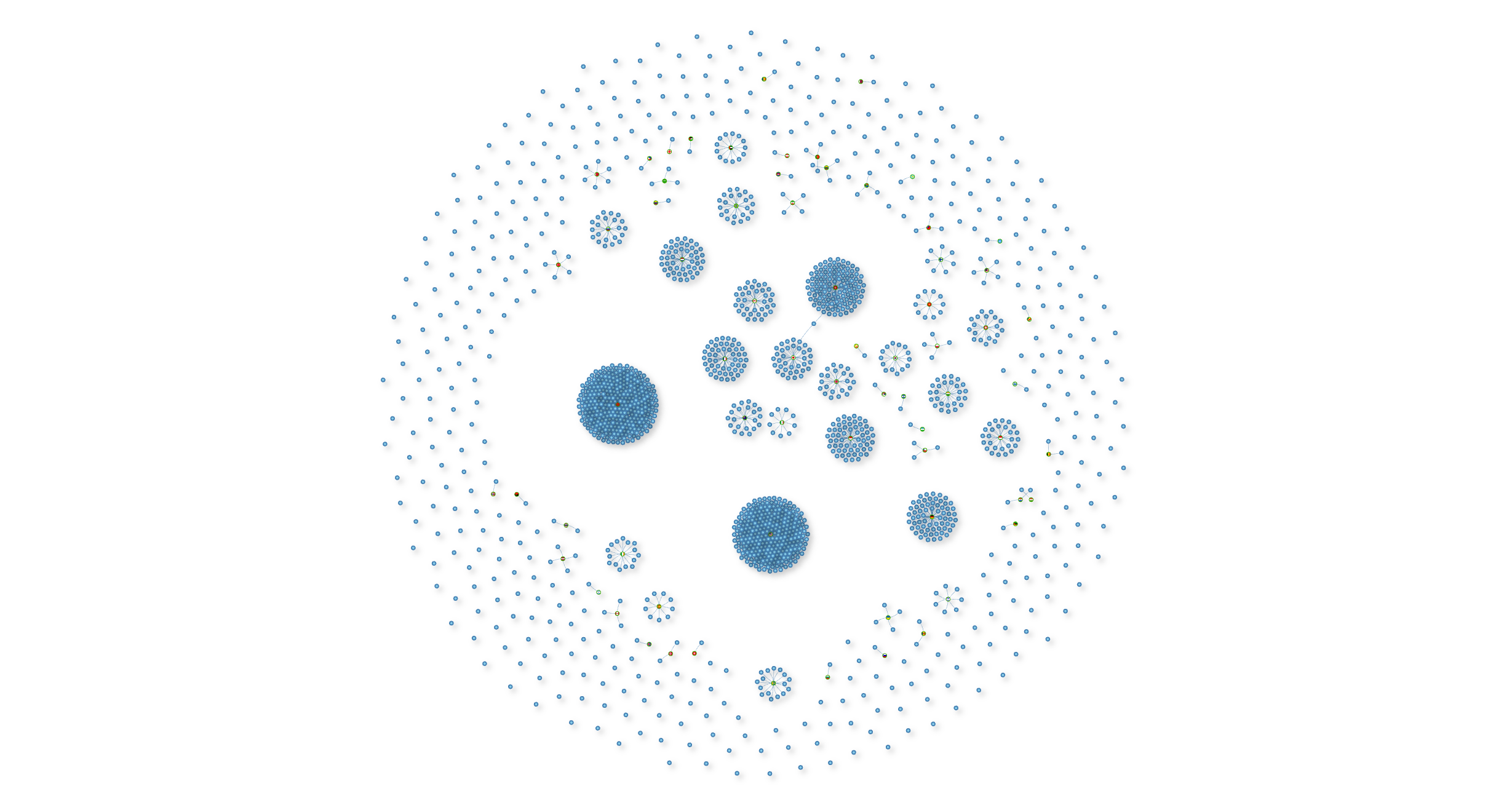
Deep dive into hackers infrastructure
Preventing cyber attacks
Minimizing the impact of cyber attacks
Protecting the infrastructure
Proactive Threat Intelligence
Unlock the full potential of research with malwareleaks
Detect and identify threats in seconds with useful features
Real-time detection
Detection time is minimized
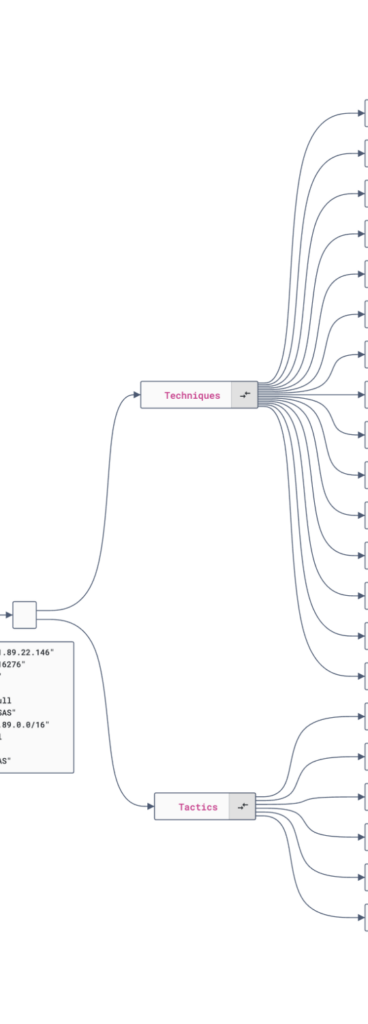
MITRE ATT&CK® Search
Finding potential threats
Map
Identify threats by location
Identifying new threats
Check now with our AI scanner
Threat Hunting
Recognize new threats
Supported security solutions
Firewalls
IDS/IPS
SIEM
WAF
Threat Feed
Integrating threat IoCs into security systems allows real-time threat detection and automated blocking of suspicious activity.
Explore the threat.
Stay ahead of cyber attacks by identifying malicious IoCs, IP, domains and malware leaks before they cause harm.
Try malwareleaks
Test all core features and see how the platform helps you solve real problems